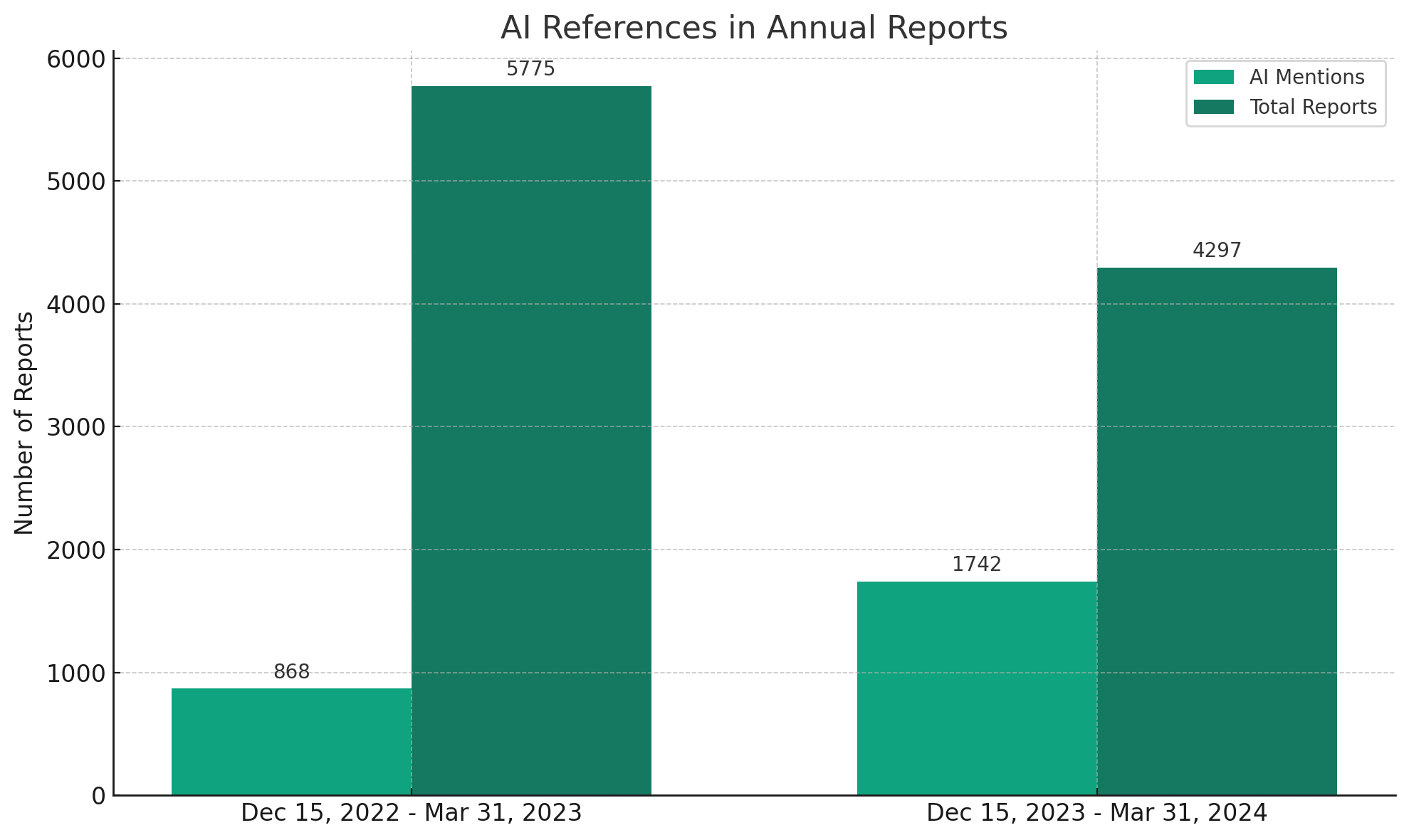
The presence of Generative Artificial Intelligence (AI) in the business world has been unmistakably marked by its burgeoning references in public company Annual 10-K Reports. A comparative analysis from December 15, 2022, to March 31, 2023, against the same period from December 15, 2023, to March 31, 2024, reveals a significant jump—from 15% to 40%—in companies mentioning AI in their Annual 10-K Reports.
This notable increase in AI references within the latest 10-K filings predominantly centers on two aspects:
- The competitive necessity to effectively incorporate AI into product offerings
- The multifaceted risks AI introduces, spanning legal, business, operational, and security domains.
The filings collectively underscore an ongoing battle between leveraging AI for market advantages and the need for its secure implementation. However, the details provided in the newly required Item 1C cybersecurity disclosures remain sparse on how companies are mitigating AI-induced cybersecurity risks.
Is There a Strategic Misalignment Between Business Goals and Cybersecurity Efforts?
Although 1,742 10-K filings identify AI as either a pivotal business concern or risk factor, only 122 10-K filings explicitly mention AI within their Item 1C cybersecurity disclosure section.
These 122 filings address AI’s role in cybersecurity through one of four narratives:
- Showcasing cybersecurity measures that employ AI for enhanced threat identification and mitigation.
- Recognizing AI as a novel risk vector that may amplify vulnerabilities in information systems.
- Demonstrating leadership’s competency in AI-related fields.
- Adapting cybersecurity governance frameworks to include standards like the NIST AI Risk Management Framework.
The bulk of AI-related cybersecurity disclosures tend to align with the first three approaches, with only a handful of companies, including a prominent semiconductor firm, citing the NIST AI Risk Management Framework as part of their cybersecurity governance.
A standout example involves a $40 billion energy company that emphasized its Artificial Intelligence Steering Committee within Item 1C. This committee is tasked with steering the strategic direction, supervision, and advisory for AI initiatives, ensuring they align with the company’s objectives, ethical standards, security protocols, and industry best practices to foster innovation and maintain competitive edge. Additionally, it regularly updates the Audit Committee on its progress.
Industry Insights
The industries most frequently mentioning AI in their Item 1C cybersecurity disclosures are:
- Manufacturing
- Finance, Insurance, and Real Estate
- Services

The distribution of AI mentions across various sectors reveals an interesting pattern, especially the underrepresentation of technology firms, which are at the forefront of AI adoption, in cybersecurity risk disclosures.
The Implications for Cybersecurity
The hallmark of a robust cybersecurity program is its ability to bolster business objectives. Yet, the data suggests a potential disconnect between perceived top business risks and the strategic response of cybersecurity risk management programs.
In future Annual 10-K Reports, companies have a significant opportunity to more effectively communicate how their cybersecurity risk strategies are aligned with their AI ambitions, and the evolving landscape of AI threats, to the investor community.
Page last updated on April 10, 2024